4 April, 2025
ESMO POSTER: Three-Year Update on the Real-World Evaluation of Colon AiQ® for Colorectal Cancer Screening in Asymptomatic Individuals
Due to the rapid development of the local economy, an aging population, and lifestyle changes, colorectal cancer (CRC) has emerged as a serious public health issue in the city of Yangzhou, China.
To address this growing health concern, a three-year prospective study (PreC Study) was conducted, aiming to evaluate the Colon AiQ® test. This non-invasive test provides a reliable approach for detecting colorectal cancer in asymptomatic individuals and increasing compliance with screening recommendations.
Study Overview:
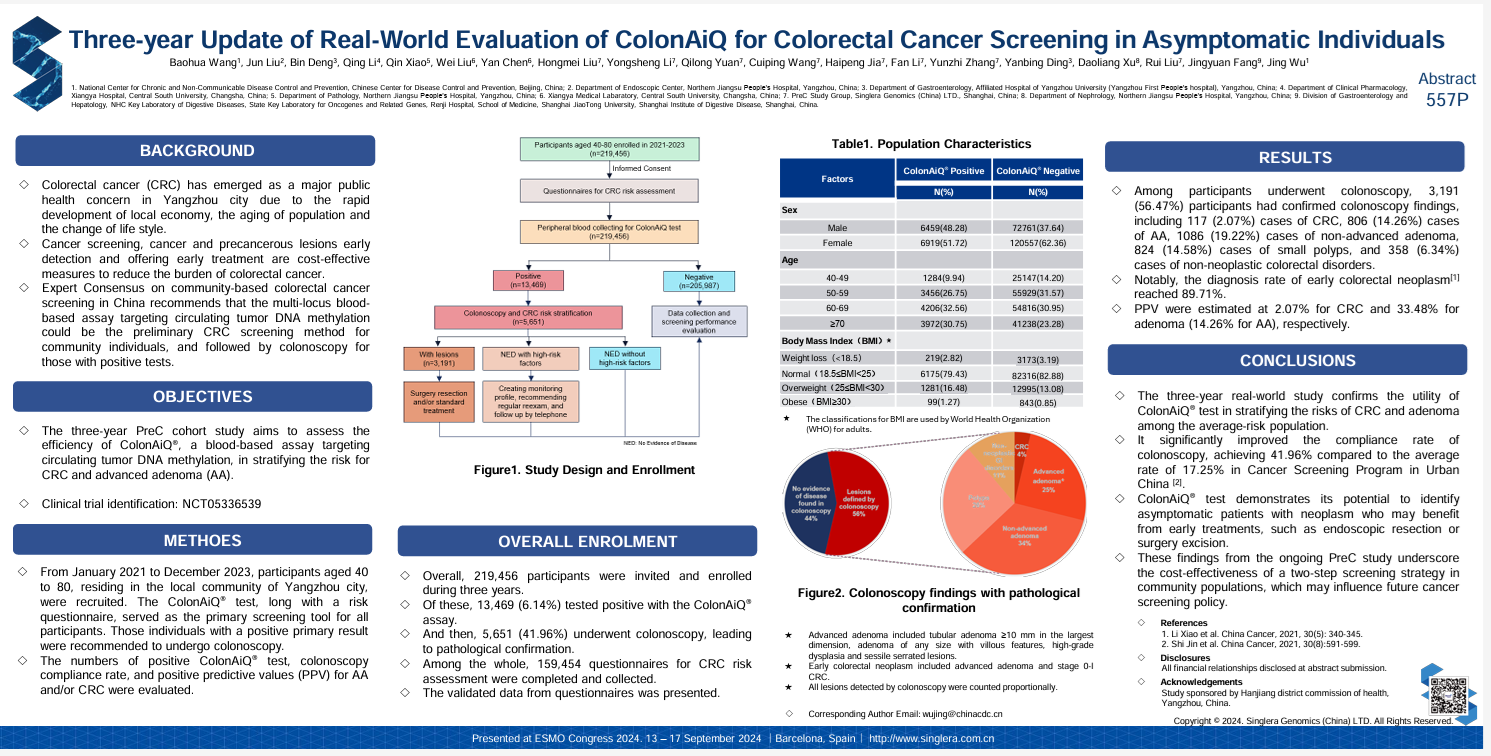
The PreC study was carried out between January 2021 and December 2023 and included 219,456 participants aged 40 to 80 from Yangzhou. All participants completed a colorectal cancer risk assessment questionnaire and then underwent the Colon AiQ® test. Individuals who tested positive were advised to undergo a colonoscopy for confirmation.
Main Objectives:
-
To evaluate the effectiveness of Colon AiQ® in detecting colorectal cancer and precancerous lesions.
-
To assess the compliance rate of individuals who tested positive with follow-up colonoscopy recommendations.
Results:
Screening and Compliance:
Out of 219,456 participants, 6.14% (13,469 individuals) tested positive with Colon AiQ®.
Of these, 41.96% (5,651 individuals) underwent colonoscopy.
This compliance rate was significantly higher than the national average of 17.25% for cancer screening programs in urban areas of China.
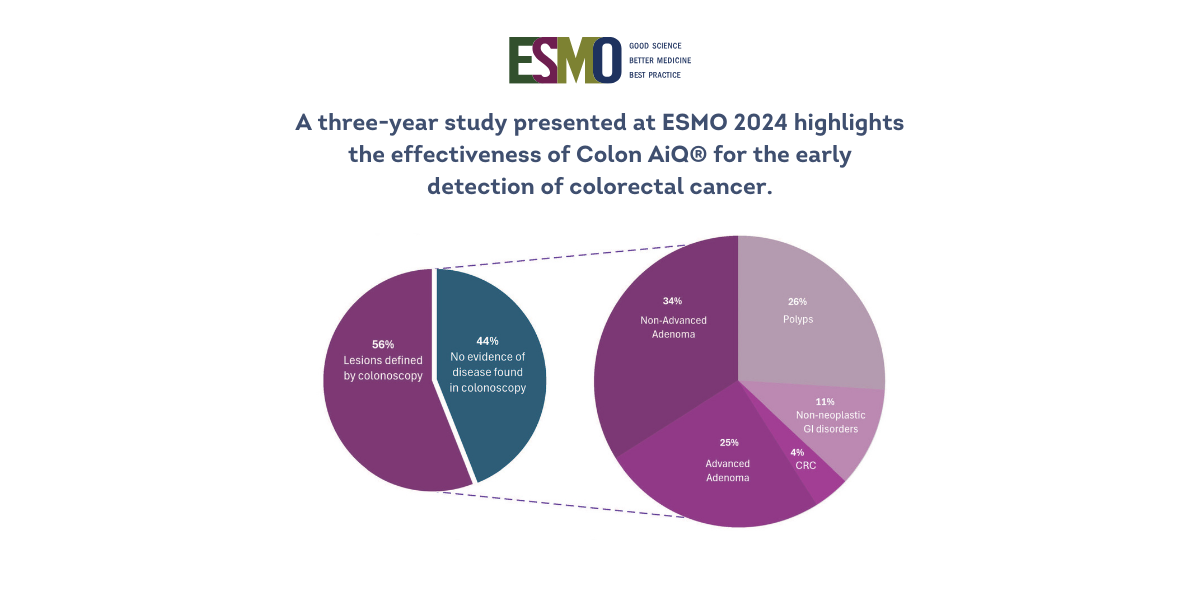
Colonoscopy Findings (among 5,651):
-
117 cases of colorectal cancer (2.07%)
-
806 cases of advanced adenomas (14.26%)
-
1,086 cases of non-advanced adenomas (19.22%)
-
824 cases of small polyps (14.58%)
-
358 cases of non-neoplastic colorectal conditions (6.34%)
Notably, 89.71% of diagnoses involved early-stage lesions, underscoring the value of early detection.
Positive Predictive Value (PPV):
Based on the findings:
- PPV for colorectal cancer: 2.07%
- PPV for adenomas overall: 33.48%, including 14.26% for advanced adenomas
PPV refers to the likelihood that a person who tests positive with Colon AiQ® actually has colorectal cancer or an adenoma — essentially, the probability that a positive test result is a true positive.
Conclusions:
In summary, this large, real-world three-year study demonstrates that Colon AiQ® is a highly effective diagnostic tool for colorectal cancer screening, particularly in population-based prevention programs. Its ability to identify high-risk individuals among asymptomatic populations supports timely intervention and helps reduce colorectal cancer morbidity and mortality.
The study also highlights the cost-effective and practical benefits of a two-step screening strategy, involving an initial non-invasive Colon AiQ® test followed by colonoscopy for positive cases. This approach not only improves compliance with screening protocols but also allows for early diagnosis and treatment of both colorectal cancer and precancerous lesions.
The ongoing PreC study underscores the importance of innovation and non-invasive screening methods, paving the way for broader implementation of such strategies in public health policies and future preventive protocols.